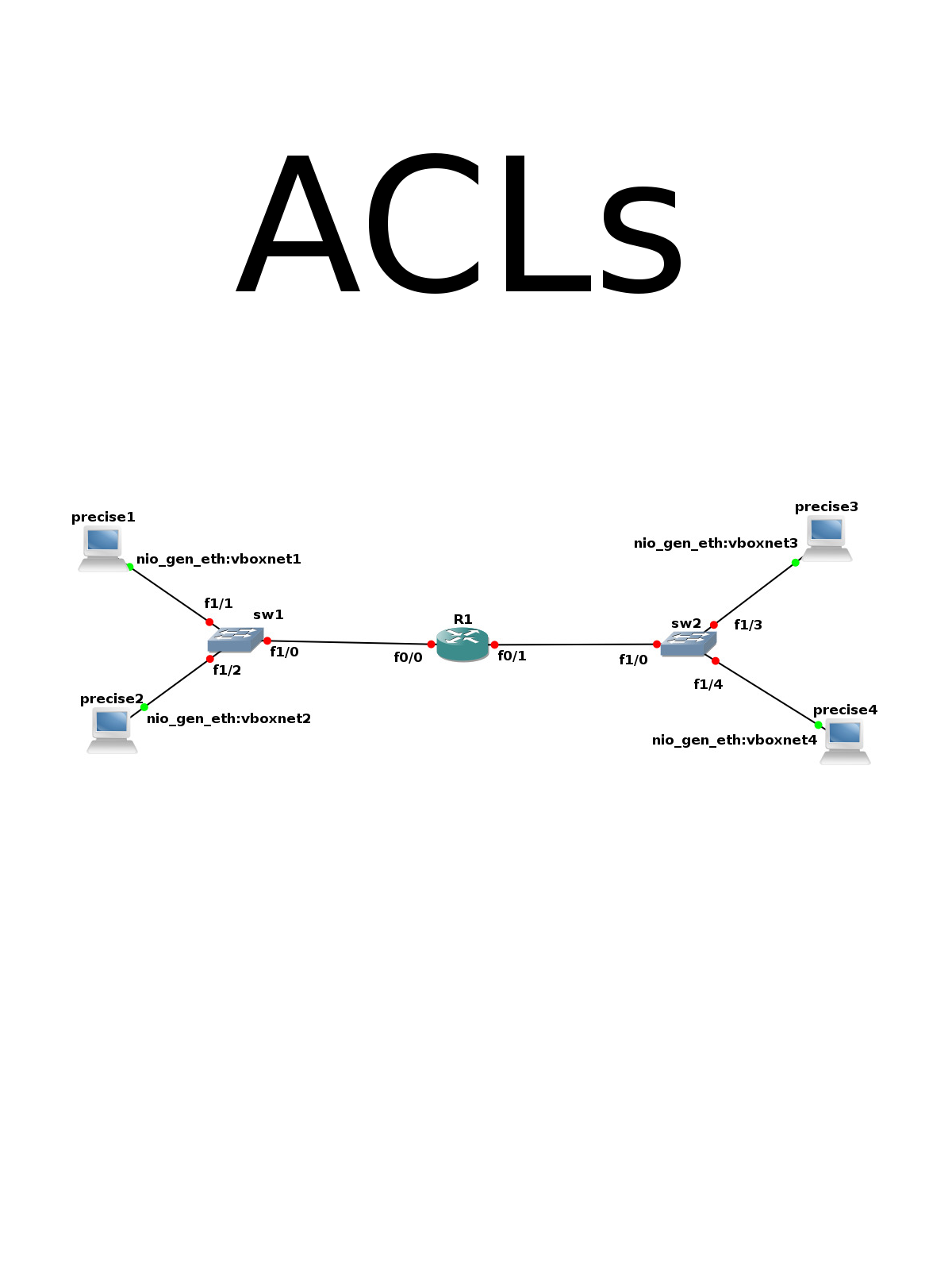
2. Setting up the server
2.1. Goal
Our goal is to set-up a server that responds to a telnet-request on a
set of ports.
This will allow us to test quickly whether a service is reachable or not.
2.2. Inetd
The simplest way to create a service on Linux is to let them be started by the
inetd
On Debian, this means installing the
inetutils-inetd.
As always, it also means that we need to disable the automatic start-up
at boot and launch it ourselves.
apt-get install inetutils-inetd rm /etc/rc*.d/*inetutils*
Next, we need to set-up a simple service that allows us to see whether we
can actually connect. Our simple service looks like this:
echo $0 $*
There are 10 versions of this file, called
/root/s900
to
/root/s909.
The following lines are added to
/etc/services
s900 900/tcp s901 901/tcp s902 902/tcp s903 903/tcp s904 904/tcp s905 905/tcp s906 906/tcp s907 907/tcp s908 908/tcp s909 909/tcp
and
we add the following lines to
/etc/inetd.conf
s900 stream tcp4 nowait root /root/vbox/acl/s900 /root/vbox/acl/s900 s901 stream tcp4 nowait root /root/vbox/acl/s901 /root/vbox/acl/s901 s902 stream tcp4 nowait root /root/vbox/acl/s902 /root/vbox/acl/s902 s903 stream tcp4 nowait root /root/vbox/acl/s903 /root/vbox/acl/s903 s904 stream tcp4 nowait root /root/vbox/acl/s904 /root/vbox/acl/s904 s905 stream tcp4 nowait root /root/vbox/acl/s905 /root/vbox/acl/s905 s906 stream tcp4 nowait root /root/vbox/acl/s906 /root/vbox/acl/s906 s907 stream tcp4 nowait root /root/vbox/acl/s907 /root/vbox/acl/s907 s908 stream tcp4 nowait root /root/vbox/acl/s908 /root/vbox/acl/s908 s909 stream tcp4 nowait root /root/vbox/acl/s909 /root/vbox/acl/s909
The
tcp4
is the protocol name. This is a non-standard in the Debian distribution. Standard
would be just
tcp
but Debian decided that that would refer to IPv6 only.
Of course, we need to install the inetd:
apt-get -y install openbsd-inetd
And then,
we can telnet into our new services:
$ vagrant ssh precise3 -c 'telnet 127.0.0.1 902' Trying 127.0.0.1... Connected to 127.0.0.1. Escape character is '^]'. /root/s902 Connection closed by foreign host. Connection to 127.0.0.1 closed.
A complete setup-script for precise1 would then be:
ETH1=$(dmesg | grep -i 'renamed from eth1' | sed -n 's/: renamed from eth1//;s/.* //p') ifconfig $ETH1 10.128.1.101 netmask 255.255.255.0 up route add -net 10.128.0.0 netmask 255.255.0.0 gw 10.128.1.1 for f in s900 s901 s902 s903 s904 s905 s906 s907 s908 s909 do cp /vagrant/service.sh /root/$f chmod a+rx /root/$f done cat >> /etc/services <<EOF s900 900/tcp s901 901/tcp s902 902/tcp s903 903/tcp s904 904/tcp s905 905/tcp s906 906/tcp s907 907/tcp s908 908/tcp s909 909/tcp EOF cat >>/etc/inetd.conf <<EOF s900 stream tcp4 nowait root /root/s900 /root/s900 s901 stream tcp4 nowait root /root/s901 /root/s901 s902 stream tcp4 nowait root /root/s902 /root/s902 s903 stream tcp4 nowait root /root/s903 /root/s903 s904 stream tcp4 nowait root /root/s904 /root/s904 s905 stream tcp4 nowait root /root/s905 /root/s905 s906 stream tcp4 nowait root /root/s906 /root/s906 s907 stream tcp4 nowait root /root/s907 /root/s907 s908 stream tcp4 nowait root /root/s908 /root/s908 s909 stream tcp4 nowait root /root/s909 /root/s909 EOF apt-get -y install openbsd-inetd ps -ef | grep inet
The
ps
is there to show that the inetd works.